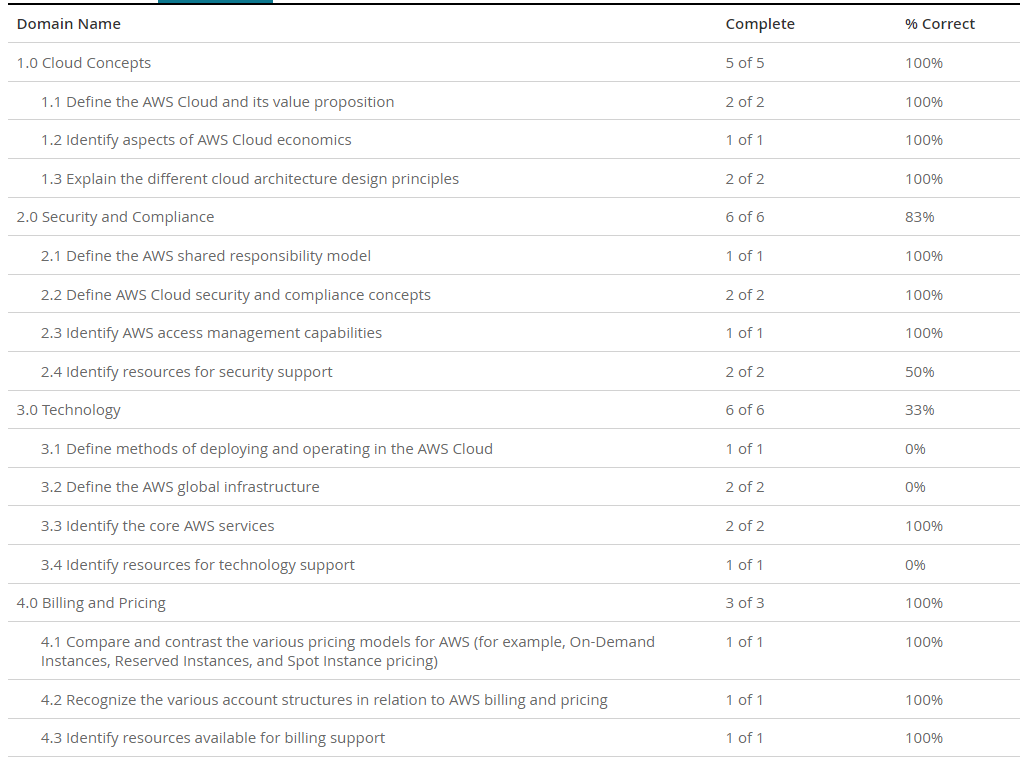
AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner
1.1 Define the AWS Cloud and its value proposition
Question 1
Which of the following are benefits of the AWS Cloud? (Select TWO.)
A - Companies need increased IT staff.
Incorrect. With the AWS Cloud, you can focus on your customers, rather than on the acquisition, installation, and management of infrastructure. Although the use of AWS services might offload some of the work your IT staff performs, it will not directly increase your IT staff.
B - Capital expenses are replaced with variable expenses.
Correct. With the AWS Cloud, you benefit from Amazon’s global purchasing of compute resources. You do not need to invest heavily in data centers.
C - Customers receive the same monthly bill regardless of which resources they use.
Incorrect. With the AWS Cloud, you pay only for the individual services that you need, for as long as you use them. You are not required to commit to a long-term contract.
For more information about flexible pricing on the AWS platform, see AWS Pricing.
D - Companies gain increased agility.
Correct. With the AWS Cloud, you make IT resources available to developers in minutes instead of weeks. The result is reduced cost and time for development, which increases agility.
For more information about agility, see Six Advantages of Cloud Computing.
E - AWS holds responsibility for security in the cloud.
Incorrect. The customer is responsible for security in the AWS Cloud as part of the AWS shared responsibility model.
For more information about security in the AWS Cloud, see Shared Responsibility Model.
Question 2
Which of the following are advantages of the AWS Cloud? (Select TWO.)
A - AWS manages the maintenance of the cloud infrastructure.
Correct. This solution is an example of security “of” the cloud. AWS is responsible for protecting the infrastructure that runs all of the services offered in the AWS Cloud. This infrastructure is composed of the hardware, software, networking, and facilities that run AWS Cloud services.
For more information about the AWS shared responsibility model, see Shared Responsibility Model.
B - AWS manages the security of applications built on AWS.
Incorrect. This solution is an example of security “in” the cloud. Application security is the customer’s responsibility.
For more information about the AWS shared responsibility model, see Shared Responsibility Model.
C - AWS manages capacity planning for physical servers.
Correct. This solution is an example of security “of” the cloud. Capacity planning of the cloud is an inherited control from AWS. AWS purchases additional servers as needed, based on overall customer demand.
For more information about the AWS shared responsibility model, see Shared Responsibility Model.
D - AWS manages the development of applications on AWS.
Incorrect. This solution is an example of security “in” the cloud. AWS does not manage application development.
For more information about the AWS shared responsibility model, see Shared Responsibility Model.
E - AWS manages cost planning for virtual servers.
Incorrect. AWS offers tools to help customers visualize, understand, and manage costs. Customers are responsible for cost planning for their virtual servers.
For more information about cost planning tools, see AWS Cost Explorer.
1.2 Identify aspects of AWS Cloud economics
Question 3
A company requires physical isolation of its Amazon EC2 instances from the instances of other customers.
Which instance purchasing option meets this requirement?
A - Dedicated Hosts
Correct. With Dedicated Hosts, a physical server is dedicated for your use. Dedicated Hosts provide visibility and the option to control how you place your instances on an isolated, physical server.
For more information about Dedicated Hosts, see Amazon EC2 Dedicated Hosts.
B - Reserved Instances
Incorrect. Reserved Instances are not physical instances. Reserved Instances are a billing discount applied to the use of On-Demand Instances in your account. Reserved Instances do not provide physical workload isolation.
For more information about Reserved Instances, see Reserved Instances.
C - On-Demand Instances
Incorrect. With On-Demand Instances, you pay for compute capacity by the second with no long-term commitments. On-Demand Instances do not provide physical workload isolation.
For more information about On-Demand Instances, see On-Demand Instances.
D - Spot Instances
Incorrect. With Spot Instances, you can take advantage of unused EC2 capacity in the AWS Cloud. Spot Instances do not provide physical workload isolation.
For more information about Spot Instances, see Amazon EC2 Spot Instances.
1.3 Explain the different cloud architecture design principles
Question 4
Which AWS Cloud architecture principle states that systems should reduce interdependencies?
A - Scalability
Incorrect. Systems that are scalable can react to increases and decreases in load. Scalability does not reduce interdependencies between system components.
For more information about AWS Cloud best practices, see AWS Well-Architected Framework.
B - Services, not servers
Incorrect. This solution does not reduce interdependencies between system components in an application deployment. However, you still need to design features that are decoupled within the application to reduce single endpoints that can become failures.
For more information about AWS Cloud best practices, see AWS Well-Architected Framework.
C - Automation
Incorrect. Automation can improve stability, efficiency during deployments, and the response to events. However, you still need to design architecture that reduces tight dependencies between the layers of the application.
For more information about AWS Cloud best practices, see AWS Well-Architected Framework.
D - Loose coupling
Correct. Loose coupling helps isolate behavior of a component from other components that depend on it, increasing resiliency and agility. A change or a failure in one of the components should not affect the other components.
For more information about AWS Cloud best practices, see AWS Well-Architected Framework.
Question 5
Which AWS Cloud architecture design principle supports the distribution of workloads across multiple Availability Zones?
A - Implement automation.
Incorrect. You can use automation services, such as AWS CloudFormation, to deploy resources into one or more Availability Zones. However, the implementation of automation is not directly tied to, or limited to, the distribution of workloads across multiple Availability Zones.
For more information about CloudFormation, see AWS CloudFormation FAQs.
B - Design for agility.
Incorrect. When you design for agility, you can provision resources more quickly. Agility is not related to the number of Availability Zones.
For more information about agility, see Risk is Lack of Agility.
C - Design for failure.
Correct. AWS recommends that you distribute workloads across multiple Availability Zones. This distribution will ensure continuous availability of your application, even if the application is unavailable in one single Availability Zone.
For more information about the performance efficiency pillar, see Performance Efficiency Pillar - AWS Well-Architected Framework.
D - Implement elasticity.
Incorrect. Elasticity is the ability to activate resources as you need them and return resources when you no longer need them. Elasticity is not related to the number of Availability Zones.
For more information about elasticity, see Elasticity.
2.1 Define the AWS shared responsibility model
Question 6
Which of the following is a responsibility of AWS under the AWS shared responsibility model?
A - Design a customer’s application for disaster recovery.
Incorrect. AWS offers many services to help with disaster recovery and business continuity planning. However, according to the shared responsibility model, it is the customer’s responsibility to decide which services it needs.
For more information about the shared responsibility model, see Shared Responsibility Model.
B - Update the guest operating systems on deployed Amazon EC2 instances.
Incorrect. The customer must manage its own updates on its provisioned infrastructure.
For more information about the shared responsibility model, see Shared Responsibility Model.
C - Configure new resources within an AWS account.
Incorrect. The customer decides which services to use and how to use them.
For more information about the shared responsibility model, see Shared Responsibility Model.
D - Secure the physical infrastructure.
Correct. AWS fully maintains the physical controls.
For more information about the shared responsibility model, see Shared Responsibility Model.
2.2 Define AWS Cloud security and compliance concepts
Question 7
Which of the following describes a security best practice that can be implemented by using AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)?
A - Turn off AWS Management Console access for all users.
Incorrect. There could be legitimate requirements for certain IAM users to have access to the console. Consequently, to turn off access for all users is not the correct solution.
For more information about best practices for securing an AWS account, see What are some best practices for securing my AWS account and its resources?
B - Generate secret keys for every IAM user.
Incorrect. This solution would generate secret keys for IAM users and would require them to access their applications through programmatic access.
For more information about best practices for securing an AWS account, see What are some best practices for securing my AWS account and its resources?
C - Grant permissions to users who are required to perform a specific task only.
Correct. Through the security recommendation of least privilege, an IAM best practice is to grant granular permissions to users by using IAM roles.
For more information about IAM best practices and least privilege, see Grant least privilege.
For more information about best practices for securing an AWS account, see What are some best practices for securing my AWS account and its resources?
D - Store AWS credentials within Amazon EC2 instances.
Incorrect. The solution to store credentials within EC2 instances is not a security best practice. It would be a better security practice to use IAM roles to grant permissions to EC2 instances, because the IAM roles will rotate the credentials automatically.
For more information about best practices for securing an AWS account, see What are some best practices for securing my AWS account and its resources?
Question 8
A company needs to monitor and receive alerts about AWS Management Console sign-in events that involve the AWS account root user.
Which AWS service can the company use to meet these requirements?
A - Amazon CloudWatch
Correct. CloudWatch monitors your AWS resources and the applications that you run on AWS in real time. You can use CloudWatch to monitor and receive alerts about console sign-in events that involve the AWS account root user.
For more information about CloudWatch, see What is Amazon CloudWatch?
B - AWS Config
Incorrect. You can use AWS Config to assess, audit, and evaluate the configurations of your AWS resources. AWS Config cannot alert you about console sign-in events that involve the AWS account root user.
For more information about AWS Config, see What is AWS Config?
C - AWS Trusted Advisor
Incorrect. You can use Trusted Advisor for real-time guidance to help you provision your resources according to AWS best practices. Trusted Advisor cannot alert you about console sign-in events that involve the AWS account root user.
For more information about Trusted Advisor, see AWS Trusted Advisor.
D - AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Incorrect. With IAM, you can manage access to AWS services and resources securely. IAM cannot alert you about console sign-in events that involve the AWS account root user.
For more information about IAM, see AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM).
2.3 Identify AWS access management capabilities
Question 9
A company has an application server that runs on an Amazon EC2 instance. The application server needs to access contents within a private Amazon S3 bucket.
What is the recommended approach to meet this requirement?
A - Create an IAM role with the appropriate permissions. Associate the role with the EC2 instance.
Correct. IAM roles are temporary credentials that expire. IAM roles are more secure than long-term access keys because they reduce risk if credentials are accidentally exposed.
For more information about IAM roles, see Using an IAM role to grant permissions to applications running on Amazon EC2 instances.
B - Configure a VPC peering connection to allow private communication between the EC2 instance and the S3 bucket.
Incorrect. A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them by using private IPv4 addresses or IPv6 addresses. VPC peering connections cannot connect a VPC and an S3 bucket.
For more information about VPC peering, see What is VPC peering?
C - Create a shared access key. Configure the EC2 instance to use the hardcoded key.
Incorrect. The creation of a shared key is not a best practice because this reduces the value of auditing AWS resource access. It is not a best practice to embed access keys into the application code because application code can become compromised.
For more information about managing access keys, see Best practices for managing AWS access keys.
D - Configure the application to read an access key from a secured source.
Incorrect. It is a best practice to use IAM roles instead of long-term access keys. Long-term access keys, such as those associated with IAM users and AWS account root users, remain valid until you manually revoke them. However, temporary security credentials that are obtained through IAM roles and other features of AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS) expire after a short period of time. Use temporary security credentials to help reduce the risk in case credentials are accidentally exposed.
For more information about managing access keys, see Best practices for managing AWS access keys.
2.4 Identify resources for security support
Question 10
Which security-related services or features does AWS offer? (Select TWO.)
A - Complete PCI compliance for customer applications that run on AWS
Incorrect. Customers are responsible for the certification of PCI compliance of their applications. Some AWS services are certified to be PCI compliant.
For more information about AWS Security Competency Partners, see AWS Security Competency Partners.
B - AWS Trusted Advisor security checks
Correct. Trusted Advisor draws upon best practices learned from serving hundreds of thousands of AWS customers. These best practices include security checks.
For more information about Trusted Advisor, see AWS Trusted Advisor.
For more information about Trusted Advisor security checks, see AWS Trusted Advisor best practice checklist.
C - Data encryption
Correct. Many AWS services support data encryption, including Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) and Amazon S3.
For more information about data encryption on Amazon S3, see Protecting data using encryption.
For more information about data encryption on Amazon EBS, see Amazon EBS encryption.
D - Automated penetration testing
Incorrect. AWS does not provide automated penetration testing. AWS customers can carry out security assessments or penetration tests on their AWS infrastructure without prior approval for some services.
For more information about penetration testing, see Penetration Testing.
E - Amazon S3 copyrighted content detection
Incorrect. AWS provides copyrighted content detection.
Question 11
Which recommendations are included in the AWS Trusted Advisor checks? (Select TWO.)
A - Amazon S3 bucket permissions
Correct. Trusted Advisor checks for S3 bucket permissions in Amazon S3 with open access permissions. Bucket permissions that grant list access to everyone can result in higher than expected charges if objects in the bucket are listed by unintended users at a high frequency. Bucket permissions that grant upload and delete access to all users create potential security vulnerabilities by allowing anyone to add, modify, or remove items in a bucket. This Trusted Advisor check examines explicit bucket permissions and associated bucket policies that might override the bucket permissions.
For more information about S3 bucket permissions, see AWS Trusted Advisor best practice checklist.
B - AWS service outages for services
Incorrect. Trusted Advisor does not provide notifications for service outages. You can use the AWS Personal Health Dashboard to learn about AWS Health events that can affect your AWS services or account.
For more information about the Personal Health Dashboard, see Getting started with the AWS Personal Health Dashboard.
C - Multi-factor authentication (MFA) use on the AWS account root user
Correct. Trusted Advisor checks the root account and warns if MFA is not enabled.
For more information about Trusted Advisor, see AWS Trusted Advisor best practice checklist.
D - Available software patches for Amazon EC2 instances
Incorrect. Trusted Advisor does not provide notifications about software patches for EC2 instances.
E - Number of users in the account
Incorrect. Trusted Advisor does not provide information about the number of users in an AWS account.
3.1 Define methods of deploying and operating in the AWS Cloud
Question 12
A company wants a dedicated private connection to the AWS Cloud from its on-premises operations.
Which AWS service or feature will provide this connection?
A - AWS VPN
Incorrect. AWS VPN establishes secure connections between your on-premises networks, remote offices, client devices, and the AWS global network. AWS VPN is not a dedicated connection.
For more information about AWS VPN, see .
B - AWS PrivateLink
Incorrect. You use PrivateLink when you want to use services offered by another VPC securely within the AWS network. With PrivateLink, all network traffic stays on the global AWS backbone and never traverses the public internet. PrivateLink does not connect to on-premises operations.
For more information about PrivateLink, see AWS PrivateLink.
C - VPC endpoint
Incorrect. A VPC endpoint enables private connections between your VPC and supported AWS services and VPC endpoint services powered by PrivateLink. A VPC endpoint does not connect to on-premises operations.
For more information about VPC endpoints, see VPC endpoints.
D - AWS Direct Connect
Correct. Direct Connect provides a dedicated private connection from your premises to the AWS Cloud. Direct Connect is an alternative to using the internet to access AWS Cloud services.
For more information about Direct Connect, see AWS Direct Connect.
3.2 Define the AWS global infrastructure
Question 13
Which aspect of AWS infrastructure provides global deployment of compute and storage?
A - Multiple Availability Zones in an AWS Region
Incorrect. Availability Zones are one or more discrete data centers with redundant power, networking, and connectivity in a Region. When infrastructure is deployed across multiple Availability Zones, you can achieve a highly available deployment within the geographical location of the Region. However, this solution does not provide global deployments.
For more information about Availability Zones, see Global Infrastructure.
B - Multiple AWS Regions
Correct. A Region is a physical location where there are clusters of AWS data centers. AWS offers many different Regions where you can deploy infrastructure around the world. With the use of multiple Regions, you can achieve a global deployment of compute, storage, and databases.
For more information about Regions, see Global Infrastructure.
C - Tags
Incorrect. Tags are metadata that you can associate with AWS resources. Tags are user-defined data in the form of key-value pairs. You can use tags to manage, identify, organize, search for, and filter resources. Tags do not provide global deployments of applications and solutions.
For more information about tags, see Tagging AWS resources.
D - Resource groups
Incorrect. AWS Resource Groups is a service that you can use to manage and automate tasks on many resources at the same time. Resources in AWS are entities such as Amazon EC2 instances and Amazon S3 buckets. With Resource Groups, you can filter resources based on tags or AWS CloudFormation stacks and then perform an action against a group of resources. You do not use Resource Groups to deploy AWS resources globally.
For more information about resource groups, see What are AWS Resource Groups?
Question 14
Which AWS services or features support data replication across AWS Regions? (Select TWO.)
A - Amazon S3
Correct. Amazon S3 supports Cross-Region Replication. With Cross-Region Replication, you designate a destination S3 bucket in another Region. When Cross-Region Replication is turned on, any new object that is uploaded will be replicated to the destination S3 bucket.
For more information about Amazon S3, see Replicating objects.
B - Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
Incorrect. Amazon EBS automatically replicates data within an Availability Zone. Amazon EBS does not support Cross-Region Replication.
For more information about Amazon EBS, see Amazon Elastic Block Store.
C - Amazon EC2 instance store
Incorrect. An EC2 instance store is block storage that is attached to an EC2 instance. This storage is located on disks that are physically attached to the host computer. An instance store is ideal for temporary storage of information that changes frequently. The data that is stored on an instance store is temporary. There is no built-in mechanism to replicate data across Regions.
For more information about EC2 instance stores, see Amazon EC2 instance store.
D - AWS Storage Gateway
Incorrect. Storage Gateway connects an on-premises software appliance with cloud-based storage. Storage Gateway provides integration with data security features between your on-premises IT environment and AWS storage infrastructure such as Amazon S3. Storage Gateway does not directly support Cross-Region Replication.
For more information about Storage Gateway, see What is AWS Storage Gateway?
E - Amazon RDS
Correct. You can use Amazon RDS to host relational databases on AWS. One RDS DB instance resides in a single Region. With Amazon RDS, you can create read replicas across Regions. Amazon RDS replicates any data from the primary DB instance to the read replica across Regions.
For more information about Amazon RDS, see Working with read replicas.
3.3 Identify the core AWS services
Question 15
A company is hosting a static website from a single Amazon S3 bucket.
Which AWS service will achieve lower latency and high transfer speeds?
A - AWS Elastic Beanstalk
Incorrect. Elastic Beanstalk is a service to deploy and scale web applications and services developed with common programming languages on automatically deployed infrastructure with capacity management, load balancing, auto scaling, and monitoring. Elastic Beanstalk makes it easier to provision and support an application. Elastic Beanstalk does not reduce website latency.
For more information about Elastic Beanstalk, see What is AWS Elastic Beanstalk?
B - Amazon DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
Incorrect. DAX is used to reduce response times from a DynamoDB table from single-digit milliseconds to microseconds. DynamoDB tables cannot host static websites.
For more information about DAX, see In-Memory Acceleration with DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX).
C - Amazon Route 53
Incorrect. Route 53 is a highly available and scalable DNS web service. The three main functions of Route 53 are registering domain names, routing internet traffic to the resources for your domain, and checking the health of those resources. Route 53 can direct traffic to S3 buckets. But because the question describes only one S3 bucket, Route 53 would have only one potential route and could not reduce latency.
For more information about Route 53, see What is Amazon Route 53?
For more information about routing to S3 buckets by using Route 53, see Routing traffic to a website that is hosted in an Amazon S3 bucket.
D - Amazon CloudFront
Correct. CloudFront is a web service that speeds up the distribution of your static and dynamic web content, such as .html, .css, .js, and image files, to your users. Content is cached in edge locations. Content that is repeatedly accessed can be served from the edge locations instead of the source S3 bucket.
For more information about CloudFront, see Accelerate static website content delivery.
Question 16
Which AWS service provides a simple and scalable shared file storage solution for use with Linux-based Amazon EC2 instances and on-premises servers?
A - AWS Managed Services (AMS)
Incorrect. AMS helps you to operate your AWS infrastructure more efficiently and securely. By using AWS services and a growing library of automations, configurations, and run books, AMS can augment and optimize your operational capabilities in both new and existing AWS environments. However, AMS is not a storage service.
For more information about AMS, see AWS Managed Services.
B - Amazon S3 Glacier
Incorrect. S3 Glacier is an object store used for archiving purposes. It is not suitable for one time access.
For more information about S3 Glacier, see What Is Amazon S3 Glacier?
C - Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS)
Incorrect. Amazon EBS provides block-level storage volumes for use with EC2 instances. EBS volumes behave like raw, unformatted block devices. However, EBS volumes cannot be shared between on-premises servers and EC2 instances.
For more information about Amazon EBS, see Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS).
D - Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS)
Correct. Amazon EFS provides an elastic file system that lets you share file data without the need to provision and manage storage. It can be used with AWS Cloud services and on-premises resources, and is built to scale on demand to petabytes without disrupting applications. With Amazon EFS, you can grow and shrink your file systems automatically as you add and remove files, eliminating the need to provision and manage capacity to accommodate growth.
For more information about using Amazon EFS, see Walkthrough: Create and mount a file system on premises with AWS Direct Connect and VPN.
3.4 Identify resources for technology support
Question 17
A company needs phone, email, and chat access 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. The response time must be less than 1 hour if a production system has a service interruption.
Which AWS Support plan meets these requirements at the LOWEST cost?
A - AWS Basic Support
Incorrect. The Basic Support plan does not include chat access and phone calls.
For more information about AWS Support plans, see Compare AWS Support Plans.
B - AWS Developer Support
Incorrect. The Developer Support plan does not include chat access and phone calls. It provides email support during business hours only.
For more information about AWS Support plans, see Compare AWS Support Plans.
C - AWS Business Support
Correct. The Business Support plan provides phone, email, and chat access 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. The Business Support plan has a response time of less than 1 hour if a production system has a service interruption.
For more information about AWS Support plans, see Compare AWS Support Plans.
D - AWS Enterprise Support
Incorrect. The Enterprise Support plan provides phone, email, and chat access 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. The Enterprise Support plan has a response time of less than 15 minutes if a production system has a service interruption. However, the Enterprise Support plan is more expensive than the Business Support plan.
For more information about AWS Support plans, see Compare AWS Support Plans.
4.1 Compare and contrast the various pricing models for AWS (for example, On-Demand Instances, Reserved Instances, and Spot Instance pricing)
Question 18
Which Amazon EC2 pricing model adjusts based on supply and demand of EC2 instances?
A - On-Demand Instances
Incorrect. On-Demand Instances are offered at a set price by AWS Region.
For more information about On-Demand Instances, see Amazon EC2 On-Demand Pricing.
B - Reserved Instances
Incorrect. Reserved Instances reserve capacity at a discounted rate. The customer commits to purchase a certain amount of compute.
For more information about Reserved Instances, see Amazon EC2 Reserved Instances.
C - Spot Instances
Correct. Spot Instances are discounted more heavily when there is more capacity available in the Availability Zones.
For more information about Spot Instances, see Amazon EC2 Spot Instances.
D - Convertible Reserved Instances
Incorrect. Reserved Instances reserve capacity at a discounted rate. The customer commits to purchase a certain amount of compute. With Convertible Reserved Instances, you can change the instance family, operating system, and tenancies.
For more information about Reserved Instances, see Amazon EC2 Reserved Instances.
4.2 Recognize the various account structures in relation to AWS billing and pricing
Question 19
Which of the following is an advantage of consolidated billing on AWS?
A - Volume pricing qualification
Correct. Consolidated billing is a feature of AWS Organizations. You can combine the usage across all accounts in your organization to share volume pricing discounts, Reserved Instance discounts, and Savings Plans. This solution can result in a lower charge compared to the use of individual standalone accounts.
For more information about consolidated billing, see Consolidated billing for AWS Organizations.
B - Shared access permissions
Incorrect. Shared access permissions is a feature of roles that are developed in AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM). This solution is not related to consolidated billing.
For more information about IAM, see What is IAM?
C - Multiple bills for each account
Incorrect. The goal of consolidated billing is to have one bill for multiple accounts.
For more information about consolidated billing, see Consolidated billing for AWS Organizations.
D - Elimination of the need to tag resources
Incorrect. In consolidated billing, you can apply tags that represent business categories. This functionality helps you organize your costs across multiple services within consolidated billing.
For more information about how tagging relates to billing, see Using Cost Allocation Tags.
4.3 Identify resources available for billing support
Question 20
Which AWS service can create an alarm that sends a notification when a billing threshold is exceeded?
A - AWS Trusted Advisor
Incorrect. Trusted Advisor draws upon best practices learned from serving hundreds of thousands of AWS customers. Trusted Advisor inspects your AWS environment and then makes recommendations when opportunities exist to save money, improve system availability and performance, or help close security gaps. However, Trusted Advisor cannot create a billing alarm.
For more information about Trusted Advisor, see AWS Trusted Advisor.
B - AWS CloudTrail
Incorrect. CloudTrail is an AWS service that helps you enable governance, compliance, and operational and risk auditing of your AWS account. CloudTrail records actions taken by a user, role, or an AWS service as events. However, CloudTrail cannot create a billing alarm.
For more information about CloudTrail, see What Is AWS CloudTrail?
C - Amazon CloudWatch
Correct. You can monitor your estimated AWS charges by using CloudWatch. When you enable the monitoring of estimated charges for your AWS account, the estimated charges are calculated and sent several times daily to CloudWatch as metric data.
For more information about CloudWatch, see Creating a billing alarm to monitor your estimated AWS charges.
D - Amazon QuickSight
Incorrect. QuickSight is a cloud-scale business intelligence (BI) service that you can use to deliver easy-to-understand insights. QuickSight connects to your data in the cloud and combines data from many different sources. However, QuickSight is a data visualization tool, not a tool for creating alarms.
For more information about QuickSight, see What Is Amazon QuickSight?
AWS Certified Developer - Associate
1.3 Prepare the application deployment package to be deployed to AWS.
1/20 0.0% complete
A developer is preparing a deployment package for a Java implementation of an AWS Lambda function.
What should the developer include in the deployment package? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A Compiled application code
Correct. To create a Lambda function, you first create a Lambda function deployment package. This deployment package is a .zip or .jar file consisting of your code and any dependencies.
For more information about Lambda deployment packages, see Lambda deployment packages.
For more information about deploying a Lambda application, see Creating an application with continuous delivery in the Lambda console.
B Java runtime environment
Incorrect. Lambda provides Java runtime, so there is no need to include it in the deployment package.
For more information about building Lambda functions with Java, see Building Lambda functions with Java.
C References to the event sources
Incorrect. The event sources are external to Lambda and are used to invoke a Lambda function. As such, event sources are not part of a Lambda deployment package.
For more information about event source mapping in Lambda, see AWS Lambda event source mappings.
D Lambda execution role
Incorrect. A Lambda execution role is an IAM role that grants the function permission to access AWS services and resources. This role is provided when a Lambda function is created. It is not included in the deployment package.
For more information about Lambda execution roles, see AWS Lambda execution role.
E Application dependencies
Correct. To create a Lambda function, you first create a Lambda function deployment package. This package is a .zip or .jar file consisting of your code and any dependencies.
For more information about Lambda deployment packages, see Lambda deployment packages.
For more information about deploying a Lambda application, see Creating an application with continuous delivery in the Lambda console.
Incorrect
CD
AE
1.3 Prepare the application deployment package to be deployed to AWS. This Question: 00:33 Total: 01:31
2/20 5.0% complete
A developer uses AWS CodeDeploy to deploy a Python application to a fleet of Amazon EC2 instances that run behind an Application Load Balancer. The instances run in an Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group across multiple Availability Zones.
What should the developer include in the CodeDeploy deployment package?
Report Content Errors
A A launch template for the Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group
Incorrect. A launch template for the Auto Scaling group is configured in Amazon EC2 AutoScaling. It is not configured in a CodeDeploy package.
For more information about Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling and how to configure it, see What is Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling?
For more information about Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling with a tutorial, see Getting started with Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling.
B A CodeDeploy AppSpec file
Correct. The CodeDeploy AppSpec (application specific) file is unique to CodeDeploy. The AppSpec file is used to manage each deployment as a series of lifecycle event hooks, which are defined in the file.
For more information about AppSpec files, see CodeDeploy application specification (AppSpec) files.
C An EC2 role that grants the application access to AWS services
Incorrect. An IAM policy by itself does not grant access to AWS services. The policy must be assigned to an IAM role. The role must be assigned to the instances to provide access.
For more information about IAM roles, see IAM roles.
For more information about IAM roles on EC2 instances, see IAM roles for Amazon EC2.
D An IAM policy that grants the application access to AWS services
Incorrect. An IAM policy that grants access to AWS services is attached to IAM users, groups, or roles. You cannot attach an IAM policy to an application.
For more information about IAM policies, see Policies and permissions in IAM.
Correct
B
B
1.4 Deploy serverless applications. This Question: 01:49 Total: 03:20
3/20 10.0% complete
A company is working on a project to enhance its serverless application development process. The company hosts applications on AWS Lambda. The development team regularly updates the Lambda code and wants to use stable code in production.
Which combination of steps should the development team take to configure Lambda functions to meet both development and production requirements? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A Create a new Lambda version every time a new code release needs testing.
Correct. Lambda function versions are designed to manage deployment of functions. They can be used for code changes, without affecting the stable production version of the code.
For more information about Lambda function versions, see Lambda function versions.
B Create two Lambda function aliases. Name one as Production and the other as Development. Point the Production alias to a production-ready unqualified Amazon Resource Name (ARN) version. Point the Development alias to the $LATEST version.
Correct. By creating separate aliases for Production and Development, systems can initiate the correct alias as needed. A Lambda function alias can be used to point to a specific Lambda function version. Using the functionality to update an alias and its linked version, the development team can update the required version as needed. The $LATEST version is the newest published version.
For more information about Lambda function aliases, see Lambda function aliases.
For more information about Lambda function versions, see Lambda function versions.
C Create two Lambda function aliases. Name one as Production and the other as Development. Point the Production alias to the production-ready qualified Amazon Resource Name (ARN) version. Point the Development alias to the variable LAMBDA_TASK_ROOT.
Incorrect. A Lambda function alias can only point to an unqualified function ARN. LAMBDA_TASK_ROOT is a variable used by Lambda to record the path to the code. However, it cannot be used in the way the response describes.
For more information about Lambda function versions, see Lambda function versions.
For more information about Lambda variables, see Configuring environment variables.
D Create a new Lambda layer every time a new code release needs testing.
Incorrect. Using a Lambda layer, you can access additional code and content. It is not suitable for code updates.
For more information about Lambda layers, see Creating and sharing Lambda layers.
E Create two Lambda function aliases. Name one as Production and the other as Development. Point the Production alias to a production-ready Lambda layer Amazon Resource Name (ARN). Point the Development alias to the $LATEST layer ARN.
Incorrect. Using a Lambda layer, you can access additional code and content. It is not suitable for code updates. Additionally, a Lambda function alias points to a Lambda function version.
For more information about Lambda layers, see Creating and sharing Lambda layers. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/lambda/latest/dg/configuration-layers.html
For more information about Lambda function aliases, see Lambda function aliases.
Correct
AB
AB
1.4 Deploy serverless applications. This Question: 01:08 Total: 04:29
4/20 15.0% complete
Each time a developer publishes a new version of an AWS Lambda function, all the dependent event source mappings need to be updated with the reference to the new version’s Amazon Resource Name (ARN). These updates are time consuming and error-prone.
Which combination of actions should the developer take to avoid performing these updates when publishing a new Lambda version? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A Update event source mappings with the ARN of the Lambda layer.
Incorrect. A Lambda event source mapping can either point to the version ARN, or an alias ARN, but not to the layer ARN.
For more information about managing Lambda function versions by using an ARN, see Lambda function versions.
For more information about creating and using Lambda function aliases, see Lambda function aliases.
For more information about Lambda layers, see Creating and sharing Lambda layers.
B Point a Lambda alias to a new version of the Lambda function.
Correct. A Lambda alias is a pointer to a specific Lambda function version.
For more information about creating and using Lambda function aliases, see Lambda function aliases.
C Create a Lambda alias for each published version of the Lambda function.
Incorrect. This solution does not address your problem. Every alias has its own unique ARN. Therefore, you would still need to update the event source mapping with the new ARN when a new version is published.
For more information about creating and using Lambda function aliases, see Lambda function aliases.
D Point a Lambda alias to a new Lambda function alias.
Incorrect. A Lambda alias cannot point to another Lambda alias, only to a Lambda function version.
For more information about Lambda function aliases, including their creation and management, see Using aliases.
E Update the event source mappings with the Lambda alias ARN.
Correct. Instead of using ARNs for the Lambda function in event source mappings, you can use an alias ARN. You do not need to update your event source mappings when you promote a new version or roll back to a previous version.
For more information about creating and using Lambda function aliases, see Lambda function aliases.
Incorrect
BC
BE
2.1 Make authenticated calls to AWS services. This Question: 00:23 Total: 04:53
5/20 20.0% complete
An application that runs on Amazon EC2 instances needs credentials to make an API call to Amazon DynamoDB.
What is the MOST secure method to provide credentials to perform the call?
Report Content Errors
A Create a user and a password with the needed permissions. Store the credentials in a configuration file on the EC2 instances.
Incorrect. You could store AWS credentials directly within the EC2 instances and allow applications that run on those instances to use those credentials. However, you would have to manage the credentials. You would have to securely pass the credentials to each instance and update each instance when it is time to rotate the credentials. This approach is not the most secure solution.
For more information about using an IAM role to grant permissions to applications running on EC2 instances, see Use roles for applications that run on Amazon EC2 instances. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html#use-roles-with-ec2
B Assign an IAM role with the correct permissions to the DynamoDB table.
Incorrect. While roles are the most secure way to provide these credentials, it is the EC2 instance that is making the API call. The instances, not the DynamoDB table, need to be assigned the proper credentials.
For more information about using an IAM role to grant permissions to applications running on EC2 instances, see Use roles for applications that run on Amazon EC2 instances. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/IAM/latest/UserGuide/best-practices.html#use-roles-with-ec2
C Assign an IAM role with the correct permissions to the EC2 instances.
Correct. The most secure method is to create an IAM role with the appropriate policy. Attach that IAM role to the EC2 instance that is making the API call. Long-term credentials are not stored, which reduces risk of compromising the credentials.
For more information about using an IAM role to grant permissions to applications running on EC2 instances, see Use roles for applications that run on Amazon EC2 instances.
D Add the name of an IAM policy with the correct permissions to a configuration file on the instances.
Incorrect. IAM policies are associated with IAM identities (users, groups, or roles) or AWS resources. A configuration file of instances is not an IAM identity or an AWS resource. Therefore, an IAM policy cannot be associated with it.
For more information about IAM policies and permission, see Policies and permissions in IAM.
Incorrect
B
C
2.2 Implement encryption using AWS services. This Question: 01:17 Total: 06:10
6/20 25.0% complete
A company wants to store sensitive user data in Amazon S3 and encrypt this data at rest. The company must manage the encryption keys and use Amazon S3 to perform the encryption.
How can a developer meet these requirements?
Report Content Errors
A Enable default encryption for the S3 bucket by using the option for server-side encryption with customer-provided encryption keys (SSE-C).
Incorrect. The default encryption behavior for an S3 bucket can be configured to either SSE-S3 or customer master keys (CMKs) stored in AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) (SSE-KMS). Although you can upload files with SSE-C, you cannot set it as a default S3 bucket encryption.
For more information about S3 encryption, see Setting default server-side encryption behavior for Amazon S3 buckets.
B Enable client-side encryption with an encryption key. Upload the encrypted object to the S3 bucket.
Incorrect. Client-side encryption involves encrypting data before sending it to Amazon S3. This solution does not meet the requirement for Amazon to provide the encryption.
For more information about client-side encryption for S3 buckets, see Protecting data using client-side encryption.
C Enable server-side encryption with Amazon S3 managed encryption keys (SSE-S3). Upload an object to the S3 bucket.
Incorrect. SSE-S3 uses an encryption key provided by Amazon S3 to encrypt data. This solution does not meet the requirement for the company to manage the encryption keys.
D Enable server-side encryption with customer-provided encryption keys (SSE-C). Upload an object to the S3 bucket.
Correct. When you upload an object, Amazon S3 uses the encryption key you provide to apply AES-256 encryption to your data and removes the encryption key from memory.
For more information about server-side encryption for S3 buckets, see Protecting data using server-side encryption with customer-provided encryption keys (SSE-C).
Incorrect
A
D
2.2 Implement encryption using AWS services. This Question: 01:29 Total: 07:40
7/20 30.0% complete
A company is developing a Python application that submits data to an Amazon DynamoDB table. The company requires client-side encryption of specific data items and end-to-end protection for the encrypted data in transit and at rest.
Which combination of steps will meet the requirement for the encryption of specific data items? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A Generate symmetric encryption keys with AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS).
Correct. When the DynamoDB Encryption Client is configured to use AWS KMS, it uses a customer master key (CMK) that is always encrypted when used outside of AWS KMS. This cryptographic materials provider returns a unique encryption key and signing key for every table item. This method of encryption uses a symmetric CMK.
For more information about the Direct KMS Materials Provider used by the DynamoDB Encryption Client, see Direct KMS Materials Provider.
For more information about CMKs, see AWS Key Management Service concepts.
B Generate asymmetric encryption keys with AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS).
Incorrect. When the DynamoDB Encryption Client is configured to use AWS KMS, it uses a customer master key (CMK) that is always encrypted when used outside of AWS KMS. This cryptographic materials provider returns a unique encryption key and signing key for every table item. This method of encryption would require a symmetric CMK, not an asymmetric key.
For more information about the Direct KMS Materials Provider, see Direct KMS Materials Provider.
For more information about CMKs, see AWS Key Management Service concepts.
C Use generated keys with the DynamoDB Encryption Client.
Correct. The DynamoDB Encryption Client provides end-to-end protection for your data in transit and at rest. You can encrypt selected items or attribute values in a table.
For more information about DynamoDB client-side and server-side encryption, see Client-side and server-side encryption.
For more information about the DynamoDB Encryption Client, see What is the Amazon DynamoDB Encryption Client?
For more information about DynamoDB Encryption Client, see How the DynamoDB Encryption Client works.
D Use generated keys to configure DynamoDB table encryption with AWS managed customer master keys (CMKs).
Incorrect. This method is used for server-side encryption at rest. This solution does not meet the requirement for client-side encryption.
For more information about DynamoDB client-side and server-side encryption, see Client-side and server-side encryption.
For more information about DynamoDB encryption at rest, see DynamoDB Encryption at Rest.
E Use generated keys to configure DynamoDB table encryption with AWS owned customer master keys (CMKs).
Incorrect. This method is used for server-side encryption at rest. This solution does not meet the requirement for client-side encryption.
For more information about DynamoDB client-side and server-side encryption, see Client-side and server-side encryption.
For more information about DynamoDB encryption at rest, see DynamoDB Encryption at Rest.
Correct
AC
AC
2.3 Implement application authentication and authorization. This Question: 02:14 Total: 09:54
8/20 35.0% complete
A company is developing a REST API with Amazon API Gateway. Access to the API should be limited to users in the existing Amazon Cognito user pool.
Which combination of steps should a developer perform to secure the API? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A Create an AWS Lambda authorizer for the API.
Incorrect. A Lambda authorizer is an API Gateway feature that uses a Lambda function to implement a custom authorization scheme to control access to your API. This solution works if the users are authenticated with OAuth or SAML. However, a Lambda authorizer does not fit this scenario.
For more information about using the Lambda authorizer, see Use API Gateway Lambda authorizers.
B Create an Amazon Cognito authorizer for the API.
Correct. An Amazon Cognito authorizer should be used for integration with Amazon Cognito user pools.
For more information about how to control access to a REST API by using Amazon Cognito user pools as an authorizer, see Control access to a REST API using Amazon Cognito user pools as authorizer.
For more information about how to integrate a REST API with an Amazon Cognito user pool, see Integrate a REST API with an Amazon Cognito user pool.
C Configure the authorizer for the API resource.
Incorrect. The authorizer cannot be configured for the API resource.
For more information about how to control access to a REST API by using Amazon Cognito user pools, see Control access to a REST API using Amazon Cognito user pools as authorizer.
D Configure the API methods to use the authorizer.
Correct. In addition to creating an authorizer, you are required to configure an API method to use that authorizer for the API.
For more information about how to configure the API methods to use the authorizer, see Control access to a REST API using Amazon Cognito user pools as authorizer.
For more information about how to integrate a REST API with an Amazon Cognito user pool, see Integrate a REST API with an Amazon Cognito user pool.
E Configure the authorizer for the API stage.
Incorrect. The authorizer cannot be configured in the API stage.
For more information about how to control access to a REST API by using Amazon Cognito user pools, see Control access to a REST API using Amazon Cognito user pools as authorizer.
Incorrect
CE
BD
2.3 Implement application authentication and authorization. This Question: 01:12 Total: 11:07
9/20 40.0% complete
A developer is implementing a mobile app to provide personalized services to app users. The application code makes calls to Amazon S3 and Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS).
Which options can the developer use to authenticate the app users? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A Authenticate to the Amazon Cognito identity pool directly.
Incorrect. The Amazon Cognito identity pool does not provide the application with user authentication service. Your application can use identity pools to exchange user pool tokens for AWS credentials.
For more information about Amazon Cognito, see What Is Amazon Cognito?
B Authenticate to AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) directly.
Incorrect. IAM does not provide the application with direct user authentication service. You use IAM users to control access to AWS.
For more information about IAM users, see IAM users.
C Authenticate to the Amazon Cognito user pool directly.
Correct. The Amazon Cognito user pool provides direct user authentication.
For more information about Amazon Cognito user pools, see Adding User Pool Sign-in Through a Third Party.
D Federate authentication by using Login with Amazon with the users managed with AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS).
Incorrect. AWS STS does not provide the application with user authentication service. It is used to request temporary credentials for IAM users. All the users would have to have IAM users, and that would be cumbersome to manage.
For more information about AWS STS, see Welcome to the AWS Security Token Service API Reference.
E Federate authentication by using Login with Amazon with the users managed with the Amazon Cognito user pool.
Correct. The Amazon Cognito user pool provides a federated authentication option with third-party identity provider (IdP), including amazon.com.
For more information about Amazon Cognito user pools, see Adding User Pool Sign-in Through a Third Party.
Incorrect
BE
CE
3.1 Write code for serverless applications. This Question: 01:15 Total: 12:22
10/20 45.0% complete
A company is implementing several order processing workflows. Each workflow is implemented by using AWS Lambda functions for each task.
Which combination of steps should a developer follow to implement these workflows? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A Define a AWS Step Functions task for each Lambda function.
Correct. Step Functions is based on state machines and tasks. A state machine is a workflow. Tasks perform work by coordinating with other AWS services, such as Lambda.
For more information about Step Functions tasks, see Task.
For more information about Step Functions, see Getting Started with AWS Step Functions.
B Define a AWS Step Functions task for each workflow.
Incorrect. A Step Functions workflow is implemented with one or more tasks.
For more information about Step Functions tasks, see Task.
C Write code that polls the AWS Step Functions invocation to coordinate each workflow.
Incorrect. You do not need to poll the Step Functions invocation to coordinate the workflow. State machines are precisely designed to coordinate the workflow.
For more information about Step Functions tasks, see Task.
For more information about Step Functions, see Getting Started with AWS Step Functions.
D Define an AWS Step Functions state machine for each workflow.
Correct. A state machine is a workflow. It can be used to express a workflow as a number of states, their relationships, and their input and output. You can coordinate individual tasks with Step Functions by expressing your workflow as a finite state machine, written in the Amazon States Language.
For more information about the Standard and Express workflows of Step Functions, see Standard and Express workflows.
For more information about states of Step Functions, see States.
E Define an AWS Step Functions state machine for each Lambda function.
Incorrect. A Step Functions state machine represents a workflow and not a Lambda function. A Lambda function would be represented as a task.
For more information about the Standard and Express workflows of Step Functions, see Standard and Express workflows.
Incorrect
AB
AD
3.2 Translate functional requirements into application design. This Question: 01:08 Total: 13:26
11/20 50.0% complete
A company is migrating a web service to the AWS Cloud. The web service accepts requests by using HTTP (port 80). The company wants to use an AWS Lambda function to process HTTP requests.
Which application design will satisfy these requirements?
Report Content Errors
A Create an Amazon API Gateway API. Configure proxy integration with the Lambda function.
Incorrect. API Gateway does not support unencrypted (HTTP) endpoints. HTTP is required in this scenario.
For more information about API Gateway endpoint protocols, see Amazon API Gateway FAQs (Q: Can I create HTTPS endpoints?)
B Create an Amazon API Gateway API. Configure non-proxy integration with the Lambda function.
Incorrect. API Gateway does not support unencrypted (HTTP) endpoints. HTTP is required in this scenario.
For more information about API Gateway endpoint protocols, see Amazon API Gateway FAQs (Q: Can I create HTTPS endpoints?)
C Configure the Lambda function to listen to inbound network connections on port 80.
Incorrect. Lambda blocks inbound network connections. Although you cannot directly invoke a Lambda function, other supported services can invoke a function.
For more information about using Lambda with other services, see Using AWS Lambda with other services.
D Configure the Lambda function as a target in the Application Load Balancer target group.
Correct. Elastic Load Balancing supports Lambda functions as a target for an Application Load Balancer. You can use load balancer rules to route HTTP requests to a function, based on the path or the header values. Then, process the request and return an HTTP response from your Lambda function.
For more information about using Lambda with an Application Load Balancer, see Using AWS Lambda with an Application Load Balancer.
Incorrect
C
D
3.2 Translate functional requirements into application design. This Question: 01:00 Total: 14:27
12/20 55.0% complete
A company is developing an image processing application. When an image is uploaded to an Amazon S3 bucket, a number of independent and separate services must be invoked to process the image. The services do not have to be available immediately, but they must process every image.
Which application design satisfies these requirements?
Report Content Errors
A Configure an Amazon S3 event notification that publishes to an Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) queue. Each service pulls the message from the same queue.
Incorrect. After a consumer retrieves and processes a message from a queue, it deletes the message in the queue. The result is that only one service receives the message.
For more information about Amazon SQS architecture, see Basic Amazon SQS architecture.
B Configure an Amazon S3 event notification that publishes to an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) topic. Each service subscribes to the same topic.
Incorrect. An Amazon SQS delivery policy defines how Amazon SNS retries the delivery of messages when a delivery error occurs. Amazon SNS stops retrying the delivery and discards the message when a delivery policy is exhausted. If one of the services is temporarily unavailable, it would not receive the message.
For more information about Amazon SNS message delivery retries, see Amazon SNS message delivery retries.
C Configure an Amazon S3 event notification that publishes to an Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) queue. Subscribe a separate Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) topic for each service to an Amazon SQS queue.
Incorrect. An Amazon SQS queue is not a supported event source for Amazon SNS.
For more information about Amazon SNS event sources, see Amazon SNS event sources.
D Configure an Amazon S3 event notification that publishes to an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) topic. Subscribe a separate Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) queue for each service to the Amazon SNS topic.
Correct. Each service can subscribe to an individual Amazon SQS queue, which receives an event notification from the Amazon SNS topic. This is a fanout architectural implementation.
For more information about Amazon SNS fanout architecture, see Common Amazon SNS scenarios.
Incorrect
A
D
3.3 Implement application design into application code. This Question: 00:53 Total: 15:20
13/20 60.0% complete
A developer wants to implement Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling for a Multi-AZ web application. However, the developer is concerned that user sessions will be lost during scale-in events.
How can the developer store the session state and share it across the EC2 instances?
Report Content Errors
A Write the sessions to an Amazon Kinesis data stream. Configure the application to poll the stream.
Incorrect. A Kinesis data stream is used for data ingestion and for processing of data records. However, it does not have the features needed for this use case. ElastiCache is better suited for this requirement.
For more information about Kinesis, see Getting started with Amazon Kinesis Data Streams.
B Publish the sessions to an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) topic. Subscribe each instance in the group to the topic.
Incorrect. Amazon SNS is used for publish-subscribe messaging. Messages are delivered as soon as they are sent. Amazon SNS is not designed to store persistent session data.
For more information about SNS, see Amazon SNS FAQs.
C Store the sessions in an Amazon ElastiCache for Memcached cluster. Configure the application to use the Memcached API.
Correct. ElastiCache for Memcached is a distributed in-memory data store or cache environment in the cloud. It will meet the developer’s requirement of persistent storage and is fast to access.
For more information about ElastiCache, see What is Amazon ElastiCache for Memcached?
For more information about Memcached, see Amazon ElastiCache for Memcached.
D Write the sessions to an Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volume. Mount the volume to each instance in the group.
Incorrect. This solution would not synchronize the session data across all instances. Amazon EBS volumes are instance specific.
Correct
C
C
3.3 Implement application design into application code. This Question: 00:44 Total: 16:04
14/20 65.0% complete
A developer is writing a component that will read customer orders from an Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) queue and process them. The developer wants to reduce empty responses to the ReceiveMessage call and obtain a customer order message as soon as it is available.
What should the developer do when writing code to retrieve messages from the queue?
Report Content Errors
A Use SQS short polling.
Incorrect. SQS short polling queries only a random subset of the servers for messages. To retrieve all messages, you might need multiple short queries. If the selected servers do not contain any messages, then empty responses would be sent. Additionally, short polling sends a response right away. These factors could result in empty responses.
For more information about SQS queries, see Amazon SQS short and long polling.
B Use SQS long polling.
Correct. SQS long polling queries all servers for messages and sends a response after it collects at least one available message. Additionally, long polling would send an empty response only if the queue is empty and the polling wait time expires.
For more information about SQS queries, see Amazon SQS short and long polling.
For more information about the ReceiveMessage API call, see ReceiveMessage.
C Extend the visibility timeout.
Incorrect. When a consumer receives and processes a message from an SQS queue, the message remains in the queue until the consumer deletes the message from the queue. To avoid other consumers from processing the same message, you can specify a visibility timeout value. A visibility timeout value is a period of time during which SQS prevents other consumers from receiving and processing the message.
For more information about visibility timeouts for Amazon SQS, see Amazon SQS visibility timeout.
D Increase the maximum number of messages to return.
Incorrect. Although a single ReceiveMessage response can include multiple messages, an increase in the MaxNumberOfMessages parameter will not ensure that all servers are queried for messages.
For more information about the ReceiveMessage API call, see ReceiveMessage.
Correct
B
B
3.4 Write code that interacts with AWS services by using APIs, SDKs, and AWS CLI. This Question: 01:17 Total: 17:22
15/20 70.0% complete
A developer is integrating a legacy web application that runs on a fleet of Amazon EC2 instances with an Amazon DynamoDB table. There is no AWS SDK for the programming language that was used to implement the web application.
Which combination of steps should the developer perform to make an API call to Amazon DynamoDB from the instances? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A Make an HTTPS POST request to the DynamoDB API endpoint for the AWS Region. In the request body, include an XML document that contains the request attributes.
Incorrect. The XML data format is not used for HTTPS-based low-level API calls.
For more information about API calls to DynamoDB, see DynamoDB Low-Level API.
B Make an HTTPS POST request to the DynamoDB API endpoint for the AWS Region. In the request body, include a JSON document that contains the request attributes.
Correct. The HTTPS-based low-level AWS API for DynamoDB uses JSON as a wire protocol format.
For more information about API calls to DynamoDB, see DynamoDB Low-Level API.
C Sign the requests by using AWS access keys and Signature Version 4.
Correct. When you send HTTP requests to AWS, you sign the requests so that AWS can identify who sent them. Requests are signed with your AWS access key, which consists of an access key ID and secret access key. AWS supports two signature versions: Signature Version 4 and Signature Version 2. AWS recommends the use of Signature Version 4.
For more information about signing AWS API requests, see Signing AWS API requests.
D Use an EC2 SSH key to calculate Signature Version 4 of the request.
Incorrect. An SSH key cannot be used to calculate Signature Version 4 of the low-level API request.
E Provide the signature value through the HTTP X-API-Key header.
Incorrect. The proper HTTP header for the signature value in low-level API calls is Authorization.
For more information about signing AWS API requests, see Signing AWS API requests.
Incorrect
BE
BC
4.1 Optimize applications to best use AWS services and features This Question: 03:14 Total: 20:36
16/20 75.0% complete
A developer has written several custom applications that read and write to the same Amazon DynamoDB table. Each time the data in the DynamoDB table is modified, this change should be sent to an external API.
Which combination of steps should the developer perform to accomplish this task? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A Configure an AWS Lambda function to poll the stream and call the external API.
Correct. If you enable DynamoDB Streams on a table, you can associate the stream Amazon Resource Name (ARN) with an Lambda function that you write. Immediately after an item in the table is modified, a new record appears in the table’s stream. Lambda polls the stream and invokes your Lambda function synchronously when it detects new stream records.
For more information about how to use DynamoDB Streams to create an event that invokes a Lambda function, see Tutorial: Process New Items with DynamoDB Streams and Lambda.
B Configure an event in Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) that publishes the change to an Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (Amazon MSK) data stream.
Incorrect. EventBridge (CloudWatch Events) is used to connect applications with a variety of data. It would not be able to detect updates to a DynamoDB table.
For more information about EventBridge (CloudWatch Events), see What Is Amazon EventBridge?
C Create a trigger in the DynamoDB table to publish the change to an Amazon Kinesis data stream.
Incorrect. A trigger cannot be enabled on a DynamoDB table. To create a trigger, a DynamoDB stream should be enabled on the specific DynamoDB table.
For more information about how to use DynamoDB Streams to create an event that invokes an AWS Lambda function, see DynamoDB Streams and AWS Lambda Triggers.
D Deliver the stream to an Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) topic and subscribe the API to the topic.
Incorrect. A DynamoDB stream cannot be used to create an Amazon SNS topic.
For more information about how to capture changes to DynamoDB tables, see Change Data Capture with Amazon DynamoDB.
For more information about how Amazon SNS works, see What is Amazon SNS?
For more information about how to create a topic in Amazon SNS, see Creating an Amazon SNS topic.
E Enable DynamoDB Streams on the table.
Correct. You can enable DynamoDB Streams on a table to create an event that invokes an AWS Lambda function.
For more information about how to use DynamoDB Streams, see DynamoDB Streams and AWS Lambda Triggers.
Incorrect
B
AE
4.2 Migrate existing application code to run on AWS. This Question: 01:13 Total: 21:50
17/20 80.0% complete
A company is migrating the create, read, update, and delete (CRUD) functionality of an existing Java web application to AWS Lambda.
Which minimal code refactoring is necessary for the CRUD operations to run in the Lambda function?
Report Content Errors
A Implement a Lambda handler function.
Correct. Every Lambda function needs a Lambda-specific handler. Specifics of authoring vary between runtimes, but all runtimes share a common programming model that defines the interface between your code and the runtime code. You tell the runtime which method to run by defining a handler in the function configuration. The runtime runs that method. Next, the runtime passes in objects to the handler that contain the invocation event and context, such as the function name and request ID.
For more information about Lambda, see Getting started with Lambda.
For more information about Lambda features, see Lambda features.
For more information about the Lambda handler function in Java, see AWS Lambda function handler in Java.
B Import an AWS X-Ray package.
Incorrect. Lambda is already integrated with X-Ray. Importing X-Ray is only needed for full instrumentation, which is optional and not part of the access control that is required by the scenario.
For more information about X-Ray, see What is AWS X-Ray?
C Rewrite the application code in Python.
Incorrect. Lambda supports Java, so you would not rewrite the code in Python. This solution would not meet the requirements of the question.
For more information about the languages that Lambda supports, see AWS Lambda FAQs.
D Add a reference to the Lambda execution role.
Incorrect. The Lambda execution role is an IAM role that grants the function permission to access AWS services and resources. The Lambda execution role exists outside the application code, so it cannot be changed by refactoring the application code.
For more information about Lambda execution roles, see AWS Lambda execution role.
Correct
A
A
5.1 Write code that can be monitored. This Question: 00:36 Total: 22:26
18/20 85.0% complete
A company plans to use AWS log monitoring services to monitor an application that runs on premises. Currently, the application runs on a recent version of Ubuntu Server and outputs the logs to a local file.
Which combination of steps should a developer perform to accomplish this goal? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A Update the application code to include calls to the agent API for log collection.
Incorrect. No update to the application code is necessary. The unified CloudWatch agent can be configured to read the local file for the log entries.
For more information about collecting metrics and logs for on-premises servers with the CloudWatch agent, see Collecting metrics and logs from Amazon EC2 instances and on-premises servers with the CloudWatch agent.
B Install the Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) container agent on the server.
Incorrect. The ECS container agent allows container instances to connect to your cluster. You do not use it for monitoring the performance of the application code.
For more information about the ECS container agent, see Amazon ECS container agent.
C Install the unified Amazon CloudWatch agent on the server.
Correct. The unified CloudWatch agent needs to be installed on the server. Ubuntu Server 18.04 is one of the many supported operating systems.
For more information about collecting metrics and logs for on-premises servers with CloudWatch agent, see Collecting metrics and logs from Amazon EC2 instances and on-premises servers with the CloudWatch agent.
D Configure the long-term AWS credentials on the server to enable log collection by the agent.
Correct. When you install the unified CloudWatch agent on an on-premises server, you will specify a named profile that contains the credentials of the IAM user.
For more information about collecting metrics and logs for on-premises servers with CloudWatch agent, see Collecting metrics and logs from Amazon EC2 instances and on-premises servers with the CloudWatch agent.
E Attach an IAM role to the server to enable log collection by the agent.
Incorrect. You cannot attach an IAM role to an on-premises server. An IAM user, not an IAM role, provides credentials for an on-premises server. An IAM role provides server credentials for Amazon EC2 instances.
For more information about collecting metrics and logs for on-premises servers with CloudWatch agent, see Collecting metrics and logs from Amazon EC2 instances and on-premises servers with the CloudWatch agent.
Incorrect
E
CD
5.1 Write code that can be monitored. This Question: 01:13 Total: 23:40
19/20 90.0% complete
A developer wants to monitor invocations of an AWS Lambda function by using Amazon CloudWatch Logs. The developer added a number of print statements to the function code that write the logging information to the stdout stream. After running the function, the developer does not see any log data being generated.
Why does the log data NOT appear in the CloudWatch logs?
Report Content Errors
A The log data is not written to the stderr stream.
Incorrect. To output logs from your function code, you can use the print method or any logging library that writes to stdout or stderr.
For more information about Lambda function logging, see AWS Lambda function logging in Python.
B Lambda function logging is not automatically enabled.
Incorrect. Lambda automatically monitors Lambda functions and reports metrics through CloudWatch. Lambda automatically tracks the number of requests, the invocation duration per request, and the number of requests that result in an error.
For more information about troubleshooting Lambda applications, see Monitoring and troubleshooting Lambda applications.
C The execution role for the Lambda function did not grant permissions to write log data to CloudWatch Logs.
Correct. The function needs permission to call CloudWatch Logs. Update the execution role to grant the permission. You can use the managed policy of AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole.
For more information about troubleshooting execution issues in Lambda, see Troubleshoot execution issues in Lambda.
D The Lambda function outputs the logs to an Amazon S3 bucket.
Incorrect. Lambda automatically stores logs generated by your code through CloudWatch Logs. You can view logs for Lambda functions by using the Lambda console, the CloudWatch console, the AWS CLI, or the CloudWatch API. You can transfer the logs from this CloudWatch log to an S3 bucket.
For more information about monitoring Lambda applications, see Monitoring and troubleshooting Lambda applications.
For more information about exporting CloudWatch Logs data from CloudWatch to Amazon S3, see Exporting log data to Amazon S3.
Correct
C
C
5.2 Perform root cause analysis on faults found in testing or production. This Question: 00:29 Total: 24:10
20/20 95.0% complete
A company notices performance degradation in one of its production web applications. The application is running on AWS services and uses a microservices architecture. The company suspects that one of these microservices is causing the performance issue.
Which AWS solution should the company use to identify the service that is contributing to higher application latency?
Report Content Errors
A AWS X-Ray service map
Correct. X-Ray creates a map of services used by your application with trace data. You can use the trace data to drill into specific services or issues. This data provides a view of connections between services in your application and aggregated data for each service, including average latency and failure rates.
For more information about X-Ray, see AWS X-Ray features.
B AWS CloudTrail event history
Incorrect. CloudTrail event history is used to record API calls for governance, compliance operation, and risk auditing purposes. CloudTrail is not a service that is used for identifying application performance issues.
For more information about CloudTrail and its uses, see What Is AWS CloudTrail?
For more information about CloudTrail event history, see Viewing Events with CloudTrail Event History.
C Amazon EventBridge (Amazon CloudWatch Events) events
Incorrect. EventBridge (CloudWatch Events) delivers a near-real-time stream of system events that describe changes in Amazon Web Services resources. It is not used for identifying application performance issues.
For more information about EventBridge (CloudWatch Events), see What Is Amazon EventBridge?
For more information about EventBridge (CloudWatch Events) events, see Amazon EventBridge events.
D AWS Trusted Advisor performance report
Incorrect. Trusted Advisor provides real-time guidance to help provision AWS resources to follow AWS best practices. It can report overall system utilization, but it is not used for identifying application performance issues.
For more information about Trusted Advisor, see AWS Trusted Advisor.
AWS
1.1 Design a multi-tier architecture solution This Question: 01:42 Total: 01:42
1/20 0.0% complete
A solutions architect is designing a solution to run a containerized web application by using Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS). The solutions architect wants to minimize cost by running multiple copies of a task on each container instance. The number of task copies must scale as the load increases and decreases.
Which routing solution distributes the load to the multiple tasks?
Report Content Errors
A Configure an Application Load Balancer to distribute the requests by using path-based routing.
Incorrect. With path-based routing, multiple services can use the same listener port on a single Application Load Balancer (ALB). The ALB forwards requests to specific target groups based on the URL path. However, this solution does not help with load distribution between different tasks of the same service.
For more information about load balancing, see Service load balancing.
B Configure an Application Load Balancer to distribute the requests by using dynamic host port mapping.
Correct. With dynamic host port mapping, multiple tasks from the same service are allowed for each container instance.
For more information about load balancing, see Service load balancing.
C Configure an Amazon Route 53 alias record set to distribute the requests with a failover routing policy.
Incorrect. You can use failover routing policies to route traffic to backup instances, in case a primary instance fails. You cannot use failover routing policies to manage multiple tasks on a single container.
For more information about routing policies, see Choosing a routing policy.
D Configure an Amazon Route 53 alias record set to distribute the requests with a weighted routing policy.
Incorrect. You can use weighted routing policies to route traffic to instances at proportions that you specify. You cannot use weighted routing policies to manage multiple tasks on a single container.
For more information about routing policies, see Choosing a routing policy.
Incorrect
D
B
1.1 Design a multi-tier architecture solution This Question: 01:45 Total: 03:28
2/20 5.0% complete
The usage of a company’s image-processing application is increasing suddenly with no set pattern. The application’s processing time grows linearly with the size of the image. The processing can take up to 20 minutes for large image files.
The architecture consists of a web tier, an Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) standard queue, and message consumers that process the images on Amazon EC2 instances. When a high volume of requests occurs, the message backlog in Amazon SQS increases. Users are reporting the delays in processing. A solutions architect must improve the performance of the application in compliance with cloud best practices.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
Report Content Errors
A Purchase enough Dedicated Instances to meet the peak demand. Deploy the instances for the consumers.
Incorrect. With Dedicated Instances, you can reduce your costs by using existing server-bound software licenses. However, server-bound licenses are not mentioned in this scenario. One of the benefits of the AWS Cloud is that you do not have to purchase for peak consumption. The AWS Cloud can scale on demand.
For more information about Dedicated Hosts, see Amazon EC2 Dedicated Hosts Pricing.
For more information about demand-based scaling, see Dynamic Supply.
B Convert the existing SQS standard queue to an SQS FIFO queue. Increase the visibility timeout.
Incorrect. FIFO queues will solve problems that occur when messages are processed out of order. FIFO queues will not improve performance during sudden volume increases. Additionally, you cannot convert SQS queues after you create them.
For more information about FIFO queues, see Amazon SQS FIFO (First-In-First-Out) queues.
For more information about SQS queues, see Editing an Amazon SQS queue (console).
C Configure a scalable AWS Lambda function as the consumer of the SQS messages.
Incorrect. Some files in this scenario can take up to 20 minutes to process. Lambda has a 15-minute operational limit.
For more information about Lambda constraints, see Lambda quotas.
D Create a message consumer that is an Auto Scaling group of instances. Configure the Auto Scaling group to scale based upon the ApproximateNumberOfMessages Amazon CloudWatch metric.
Correct. With Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling, the processing capacity can keep up with the demand.
For more information about the use of Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling with Amazon SQS, see Scaling based on Amazon SQS.
1.2 Design highly available and/or fault-tolerant architectures This Question: 00:53 Total: 04:21
3/20 10.0% complete
An application runs on two Amazon EC2 instances behind a Network Load Balancer. The EC2 instances are in a single Availability Zone.
What should a solutions architect do to make this architecture more highly available?
Report Content Errors
A Create a new VPC with two new EC2 instances in the same Availability Zone as the original EC2 instances. Create a VPC peering connection between the two VPCs
Incorrect. VPC peering will provide connectivity to the other Availability Zone. However, VPC peering does not ensure high availability because the EC2 instances are still in one Availability Zone.
For more information about VPC peering, see What is VPC Peering?
B Replace the Network Load Balancer with an Application Load Balancer that is configured with the EC2 instances in an Auto Scaling group.
Incorrect. The replacement of the Network Load Balancer with an Application Load Balancer provides no additional availability. Both load balancers are inherently highly available. However, the EC2 instances would be highly available only if they extended across two Availability Zones.
For more information about Elastic Load Balancing, see How Elastic Load Balancing works.
C Configure Amazon Route 53 to perform health checks on the EC2 instances behind the Network Load Balancer. Add a failover routing policy.
Incorrect. Failover routing requires a primary destination and a secondary (failover) destination. No failover destination is specified in this solution. In addition, this approach does not ensure high availability because the EC2 instances are still in one Availability Zone.
For more information about DNS failover, see Configuring DNS failover.
D Place the EC2 instances in an Auto Scaling group that extends across multiple Availability Zones. Designate the Auto Scaling group as the target of the Network Load Balancer.
Correct. This solution extends the EC2 instances across multiple Availability Zones and automatically adds capacity when additional capacity is needed.
For more information about Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling, see Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling benefits.
Correct
D
D
1.4 Choose appropriate resilient storage This Question: 00:56 Total: 05:17
4/20 15.0% complete
A company is using an Amazon S3 bucket to store legal documents. The company frequently revises the documents and re-uploads them with the same object key to the S3 bucket. The company needs the ability to download older copies of the documents. The company also needs to protect the documents from accidental deletion.
What is the MOST operationally efficient solution that meets these requirements?
Report Content Errors
A Enable S3 Versioning on the S3 bucket.
Correct. With S3 Versioning, you can keep multiple variants of an object in the same S3 bucket. You can use S3 Versioning to preserve, retrieve, and restore every version of every object that is stored in your S3 bucket. By using S3 Versioning, you can recover from unintended user actions and application failures.
For more information about S3 Versioning, see How S3 Versioning works.
B Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) delete on the S3 bucket.
Incorrect. MFA delete provides an additional layer of object security. MFA delete ensures that the entity that deletes the objects possesses an authorized MFA token. However, MFA delete does not meet the document versioning requirements of this question.
For more information about MFA delete, see Configuring MFA delete.
C Configure S3 Cross-Region Replication from the S3 bucket to an S3 bucket in a different AWS Region.
Incorrect. S3 Cross-Region Replication requires S3 Versioning as a prerequisite. However, S3 Versioning alone meets the requirements of this question and is the more operationally efficient solution.
For information about S3 Cross-Region Replication, see Replicating objects.
D Configure an S3 Lifecycle policy to archive the documents to S3 Glacier after 30 days.
Incorrect. You can use S3 Lifecycle rules to store objects cost-effectively throughout their lifecycle. S3 Lifecycle rules do not meet the document versioning requirements of this question.
For more information about S3 Lifecycle rules, see Managing your storage lifecycle.
Correct
A
A
2.1 Identify elastic and scalable compute solutions for a workload This Question: 00:50 Total: 06:07
5/20 20.0% complete
A reporting application runs on Amazon EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer. The instances run in an Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group across multiple Availability Zones. For complex reports, the application can take up to 15 minutes to respond to a request. A solutions architect is concerned that users will receive HTTP 5xx errors if a report request is in process during a scale-in event.
What should the solutions architect do to ensure that user requests will be completed before instances are terminated?
Report Content Errors
A Enable sticky sessions (session affinity) for the target group of the instances.
Incorrect. If an EC2 instance were removed from the target group during a scale-in process, the EC2 instance would fail (or would be unhealthy if it were checked). An Application Load Balancer would stop routing requests to that target and would choose a new healthy target.
For more information about sticky sessions, see Sticky sessions for your Application Load Balancer.
B Increase the instance size in the Application Load Balancer target group.
Incorrect. An increase of the instance size likely would increase the speed of processing. However, this solution does not directly ensure that instances that process a request are unaffected by scale-in actions.
For more information about deregistration delay, see Deregistration delay.
C Increase the cooldown period for the Auto Scaling group to a greater amount of time than the time required for the longest running responses.
Incorrect. Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling cooldown periods help you prevent Auto Scaling groups from launching or terminating additional instances before the effects of previous activities are apparent.
For more information about cooldown periods, see Scaling cooldowns for Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling.
D Increase the deregistration delay timeout for the target group of the instances to greater than 900 seconds.
Correct. By default, Elastic Load Balancing waits 300 seconds before the completion of the deregistration process, which can help in-flight requests to the target become complete. To change the amount of time that Elastic Load Balancing waits, update the deregistration delay value.
For more information about deregistration delay, see Deregistration Delay.
Incorrect
C
D
2.1 Identify elastic and scalable compute solutions for a workload This Question: 00:39 Total: 06:47
6/20 25.0% complete
A company used Amazon EC2 Spot Instances for a demonstration that is now complete. A solutions architect must remove the Spot Instances to stop them from incurring cost.
What should the solutions architect do to meet this requirement?
Report Content Errors
A Cancel the Spot request only.
Incorrect. If the only action you take is to cancel the Spot request, the running instances will not be terminated automatically. These instances will continue to run and will incur additional cost.
For more information about the termination of Spot Instances, see Terminate a Spot Instance.
B Terminate the Spot Instances only.
Incorrect. When Spot Instances are terminated, new instances will launch until the Spot request is canceled.
For more information about the termination of Spot Instances, see Terminate a Spot Instance.
C Cancel the Spot request. Terminate the Spot Instances.
Correct. To remove the Spot Instances, the appropriate steps are to cancel the Spot request and then to terminate the Spot Instances.
For more information about the termination of Spot Instances, see Terminate a Spot Instance.
D Terminate the Spot Instances. Cancel the Spot request.
Incorrect. When Spot Instances are terminated, new instances will launch until the Spot request is canceled.
For more information about the termination of Spot Instances, see Terminate a Spot Instance.
Incorrect
B
C
2.1 Identify elastic and scalable compute solutions for a workload This Question: 00:41 Total: 07:28
7/20 30.0% complete
A company needs to look up configuration details about how a Linux-based Amazon EC2 instance was launched.
Which command should a solutions architect run on the EC2 instance to gather the system metadata?
Report Content Errors
A curl http://169.254.169.254/latest/meta-data
Correct. The only way to retrieve instance metadata is to use the link-local address, which is 169.254.169.254.
For more information about instance metadata, see Retrieve instance metadata.
B curl http://localhost/latest/meta-data
Incorrect. The use of localhost will not work because this solution checks an IP address of 127.0.0.1. Metadata is not available through the use of the localhost name.
For more information about instance metadata, see Retrieve instance metadata.
C curl http://254.169.254.169/latest/meta-data
Incorrect. The format for the link-local address is 169.254.169.254.
For more information about instance metadata, see Retrieve instance metadata.
D curl http://192.168.0.1/latest/meta-data
Incorrect. The 192.168.x.x. IP address range is a public block. Instance metadata is not available through a public block.
For more information about instance metadata, see Retrieve instance metadata.
Incorrect
D
A
2.2 Select high-performing and scalable storage solutions for a workload This Question: 01:00 Total: 08:29
8/20 35.0% complete
A company has an on-premises application that exports log files about users of a website. These log files range from 20 GB to 30 GB in size. A solutions architect has created an Amazon S3 bucket to store these files. The files will be uploaded directly from the application. The network connection experiences intermittent failures, and the upload sometimes fails.
A solutions architect must design a solution that resolves this problem. The solution must minimize operational overhead.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
Report Content Errors
A Enable S3 Transfer Acceleration.
Incorrect. S3 Transfer Acceleration facilitates quicker uploads by using edge locations to copy data into Amazon S3. S3 Transfer Acceleration does not solve the problem of the file size limitation (5 GB) for a single PUT operation.
For more information about S3 Transfer Acceleration, see S3 Transfer Acceleration.
B Copy the files to an Amazon EC2 instance in the closest AWS Region. Use S3 Lifecycle policies to copy the log files to Amazon S3.
Incorrect. This solution does not solve the problem of the file size limitation (5 GB) for a single PUT operation. S3 Lifecycle policies cannot transfer files from EC2 block storage to Amazon S3. This solution also adds unnecessary services and operational overhead to the environment.
For more information about Amazon EC2, see What is Amazon EC2?
C Use multipart upload to Amazon S3.
Correct. With a single PUT operation, you can upload a single object that is up to 5 GB in size. You can use a multipart upload to upload larger files, such as the files in this scenario.
For more information about multipart uploads, see Uploading and copying objects using multipart upload.
D Upload the files to two AWS Regions simultaneously. Enable two-way Cross-Region Replication between the two Regions.
Incorrect. This solution does not solve the problem of the file size limitation (5 GB) for a single PUT operation. Each destination Region would have the same problem as a single Region. This solution also adds operational overhead.
For more information about configuring replication, see Configuring replication for source and destination buckets owned by the same account.
Correct
C
C
2.2 Select high-performing and scalable storage solutions for a workload This Question: 00:27 Total: 08:56
9/20 40.0% complete
A company is deploying a new database on a new Amazon EC2 instance. The workload of this database requires a single Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volume that can support up to 20,000 IOPS.
Which type of EBS volume meets this requirement?
Report Content Errors
A Throughput Optimized HDD
Incorrect. A Throughput Optimized HDD EBS volume is an HDD-backed storage device that is limited to 500 IOPS for each volume.
For more information about Throughput Optimized HDD EBS volumes, see Hard disk drives (HDD).
B Provisioned IOPS SSD
Correct. A Provisioned IOPS SSD EBS volume provides up to 64,000 IOPS for each volume.
For more information about Provisioned IOPS SSD EBS volumes, see Solid state drives (SSD).
C General Purpose SSD
Incorrect. A General Purpose SSD EBS volume is limited to 16,000 IOPS for each volume.
For more information about General Purpose SSD EBS volumes, see Solid state drives (SSD).
D Cold HDD
Incorrect. A Cold HDD volume provides low-cost magnetic storage that defines performance in terms of throughput rather than IOPS. Cold HDD volumes are a good fit for large, sequential cold-data workloads.
For more information about Cold HDD EBS volumes, see Amazon EBS Cold HDD Volumes.
Incorrect
C
B
2.3 Select high-performing networking solutions for a workload This Question: 00:29 Total: 09:26
10/20 45.0% complete
Which components are required to build a site-to-site VPN connection on AWS? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A An internet gateway
Incorrect. An internet gateway is attached to a VPC to allow traffic from the internet to flow into or out of the VPC. A VPN connection does not flow through an internet gateway. The internet gateway is designed to allow traffic from the open internet, not an encrypted VPN connection.
For more information about internet gateways, see Internet gateways.
B A NAT gateway
Incorrect. A NAT gateway provides a way for private Amazon EC2 instances to send requests to the internet. A NAT gateway does not give you the ability to create an encrypted site-to-site VPN connection.
For more information about NAT gateways, see NAT gateways.
For more information about VPN connections to AWS, see What is AWS Site-to-Site VPN?
C A customer gateway
Correct. A customer gateway is required for the VPN connection to be established. A customer gateway device is set up and configured in the customer’s data center.
For more information about customer gateways and VPN connections to AWS, see What is AWS Site-to-Site VPN?
D Amazon API Gateway
Incorrect. API Gateway is a fully managed service for developers to create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs at any scale. APIs act as the front door for applications to use to access data, business logic, or functionality from backend services. However, API Gateway is not necessary for the implementation of a VPN connection.
For more information about API Gateway, see What is Amazon API Gateway?
E A virtual private gateway
Correct. A virtual private gateway is attached to a VPC to create a site-to-site VPN connection on AWS. You can accept private encrypted network traffic from an on-premises data center into your VPC without the need to traverse the open public internet.
For more information about virtual private gateways and VPN connections to AWS, see What is AWS Site-to-Site VPN?
Incorrect
BE
CE
2.4 Choose high-performing database solutions for a workload This Question: 00:35 Total: 10:02
11/20 50.0% complete
A company is developing a chat application that will be deployed on AWS. The application stores the messages by using a key-value data model. Groups of users typically read the messages multiple times. A solutions architect must select a database solution that will scale for a high rate of reads and will deliver messages with microsecond latency.
Which database solution will meet these requirements?
Report Content Errors
A Amazon Aurora with Aurora Replicas
Incorrect. Aurora is a relational database (not a key-value database). Aurora is not likely to achieve microsecond latency consistently.
For more information about Aurora, see What is Amazon Aurora?
B Amazon DynamoDB with DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX)
Correct. DynamoDB is a NoSQL database that supports key-value records. DAX delivers response times in microseconds.
For more information about DynamoDB, see What is Amazon DynamoDB?
For more information about DAX, see In-Memory Acceleration with DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX).
C Amazon Aurora with Amazon ElastiCache for Memcached
Incorrect. Aurora is a relational database (not a key-value database). Aurora is not likely to achieve microsecond latency consistently, even with ElastiCache.
For more information about Aurora, see What is Amazon Aurora?
For more information about ElastiCache for Memcached, see What is Amazon ElastiCache for Memcached?
D Amazon Neptune with Amazon ElastiCache for Memcached
Incorrect. Neptune is a graph database that is optimized for working with highly connected data. Neptune is not optimized for simple key-value data.
For more information about Neptune, see What Is Amazon Neptune?
Incorrect
C
B
3.1 Design secure access to AWS resources This Question: 00:57 Total: 11:00
12/20 55.0% complete
A company uses one AWS account to run production workloads. The company has a separate AWS account for its security team. During periodic audits, the security team needs to view specific account settings and resource configurations in the AWS account that runs production workloads. A solutions architect must provide the required access to the security team by designing a solution that follows AWS security best practices.
Which solution will meet these requirements?
Report Content Errors
A Create an IAM user for each security team member in the production account. Attach a permissions policy that provides the permissions required by the security team to each user.
Incorrect. This solution does not follow the security best practice of using roles to delegate permissions.
For more information about how to use roles to delegate permissions, see Use roles to delegate permissions.
B Create an IAM role in the production account. Attach a permissions policy that provides the permissions required by the security team. Add the security team account to the trust policy.
Correct. This solution follows security best practices by using a role to delegate permissions that consist of least privilege access.
For more information about how to use roles to delegate permissions, see Use roles to delegate permissions.
C Create a new IAM user in the production account. Assign administrative privileges to the user. Allow the security team to use this account to log in to the systems that need to be accessed.
Incorrect. The assignment of administrative privileges to a user violates security best practices and the principle of least privilege.
For more information about how to grant least privilege in roles, see Grant least privilege.
D Create an IAM user for each security team member in the production account. Attach a permissions policy that provides the permissions required by the security team to a new IAM group. Assign the security team members to the group.
Incorrect. This solution does not follow the security best practice of using roles to delegate permissions.
For more information about how to use roles to delegate permissions, see Use roles to delegate permissions.
Incorrect
D
B
3.1 Design secure access to AWS resources This Question: 00:31 Total: 11:31
13/20 60.0% complete
A company is developing a new mobile version of its popular web application in the AWS Cloud. The mobile app must be accessible to internal and external users. The mobile app must handle authorization, authentication, and user management from one central source.
Which solution meets these requirements?
Report Content Errors
A IAM roles
Incorrect. An IAM role is an IAM entity that is assumable by an IAM user. An IAM role has permissions policies that define what the entity can and cannot do. However, an IAM role does not control access to an application.
For more information about IAM roles, see IAM roles.
B IAM users and groups
Incorrect. You can use IAM users and groups to control who is authenticated and authorized to use an AWS service. However, users and groups do not control access to an application.
For more information about IAM users, see IAM users.
For more information about IAM groups, see IAM groups.
C Amazon Cognito user pools
Correct. Amazon Cognito provides authentication, authorization, and user management for your web and mobile apps. Users can sign in directly with a user name and password, or through a trusted third party.
For more information about Amazon Cognito, see What is Amazon Cognito?
D AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS)
Incorrect. You can use AWS STS to create and provide trusted users with temporary security credentials that can control access to your AWS resources. However, AWS STS does not control access to an application.
For more information about temporary security credentials, see Temporary security credentials in IAM.
Incorrect
B
C
3.2 Design secure application tiers This Question: 00:58 Total: 12:29
14/20 65.0% complete
A company has strict data protection requirements. A solutions architect must configure security for a VPC to ensure that backend Amazon RDS DB instances cannot be accessed from the internet. The solutions architect must ensure that the DB instances are accessible from the application tier over a specified port only.
Which actions should the solutions architect take to meet these requirements? (Select TWO.)
Report Content Errors
A Specify a DB subnet group that contains only private subnets for the DB instances.
Correct. A private subnet is one component to use to secure the database tier. Internet traffic is not routed to a private subnet. When you place DB instances in a private subnet, you add a layer of security.
For more information about VPCs with public subnets and private subnets, see Routing.
B Attach an elastic network interface with a private IPv4 address to each DB instance.
Incorrect. An elastic network interface is a logical networking component in a VPC that represents a virtual network card. The use of an elastic network interface would not meet the requirements in the scenario.
For more information about elastic network interfaces, see Elastic network interfaces.
C Configure AWS Shield with the VPC. Update the route tables for the subnets that the DB instances use.
Incorrect. Shield provides protection against DDoS attacks. Shield cannot be a target of routes in a route table. The use of Shield would not meet the requirements in the scenario.
For more information about Shield, see AWS Shield.
D Configure an AWS Direct Connect connection on the database port between the application tier and the backend.
Incorrect. Direct Connect provides a dedicated connection to your AWS environment. The use of Direct Connect would not meet the requirements in the scenario.
For more information about Direct Connect, see AWS Direct Connect features.
E Add an inbound rule to the database security group that allows requests from the security group of the application tier over the database port. Remove other inbound rules.
Correct. Security groups can restrict access to the DB instances. Security groups provide access from only the application tier on only a specific port.
For more information about security groups, see Security group basics.
Incorrect
AC
AE
3.3 Select appropriate data security options This Question: 01:00 Total: 13:30
15/20 70.0% complete
A company runs its website on Amazon EC2 instances behind an Application Load Balancer that is configured as the origin for an Amazon CloudFront distribution. The company wants to protect against cross-site scripting and SQL injection attacks.
Which approach should a solutions architect recommend to meet these requirements?
Report Content Errors
A Enable AWS Shield Advanced. List the CloudFront distribution as a protected resource.
Incorrect. Shield Advanced protects against DDoS attacks. Shield Advanced does not protect against cross-site scripting or SQL injection.
For more information about Shield Advanced, see AWS Shield.
B Define an AWS Shield Advanced policy in AWS Firewall Manager to block cross-site scripting and SQL injection attacks.
Incorrect. With Firewall Manager, you can manage AWS WAF, Shield Advanced, and other AWS services. Shield Advanced protects against DDoS attacks. Shield Advanced does not protect against cross-site scripting or SQL injection.
For more information about AWS WAF, AWS Shield, and Firewall Manager, see What are AWS WAF, AWS Shield, and AWS Firewall Manager?
C Set up AWS WAF on the CloudFront distribution. Use conditions and rules that block cross-site scripting and SQL injection attacks.
Correct. AWS WAF can detect the presence of SQL code that is likely to be malicious (known as SQL injection). AWS WAF also can detect the presence of a script that is likely to be malicious (known as cross-site scripting).
For more information about AWS WAF, see AWS WAF.
D Deploy AWS Firewall Manager on the EC2 instances. Create conditions and rules that block cross-site scripting and SQL injection attacks.
Incorrect. With Firewall Manager, you can manage AWS WAF, AWS Shield Advanced, and other AWS services. Firewall Manager is a managed service that is not installed on EC2 instances.
For more information about Firewall Manager, see Firewall Manager.
Incorrect
B
C
4.1 Identify cost-effective storage solutions This Question: 01:19 Total: 14:50
16/20 75.0% complete
A solutions architect is planning a company’s migration to the AWS Cloud. A key component of the company’s environment is an application server that sends email notifications to customers. As part of this migration, the solutions architect must use only managed AWS services.
Which solution meets these requirements?
Report Content Errors
A Configure Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) with a standard queue.
Incorrect. Amazon SQS is a fully managed message queuing service that sends messages between software components. However, Amazon SQS cannot push messages to customers.
For information about Amazon SQS, see Amazon Simple Queue Service.
B Deploy an Amazon EC2 instance to host the application server. Send email notifications.
Incorrect. The deployment of an EC2 instance gives the company the ability to run its application. However, this solution does not use only managed services.
For more information about Amazon EC2, see Amazon EC2.
C Configure Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) with a FIFO queue.
Incorrect. Amazon SQS is a fully managed message queuing service that sends messages between software components. However, Amazon SQS cannot push messages to customers.
For information about Amazon SQS, see Amazon Simple Queue Service.
D Configure Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) with the protocol of email.
Correct. Amazon SNS is a fully managed messaging service for application-to-application communication and application-to-person communication.
For more information about Amazon SNS, see Amazon SNS FAQs.
Correct
D
D
4.1 Identify cost-effective storage solutions This Question: 00:42 Total: 15:32
17/20 80.0% complete
A company needs to maintain data records for a minimum of 5 years. The data is rarely accessed after it is stored. The data must be accessible within 2 hours.
Which solution will meet these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
Report Content Errors
A Store the data in an Amazon Elastic File System (Amazon EFS) file system. Access the data by using AWS Direct Connect.
Incorrect. This solution is not the most cost-effective solution. Amazon S3 is a more cost-effective solution if there is not a requirement for a file system.
For more information about Amazon EFS and Direct Connect, see How Amazon EFS works with AWS Direct Connect and AWS Managed VPN.
B Store the data in an Amazon S3 bucket. Use an S3 Lifecycle policy to move the data to S3 Glacier.
Correct. The storage of the data in an S3 bucket provides a cost-effective initial location for the data. S3 Glacier is the most cost-effective archival storage solution that meets the requirement of a 2-hour retrieval time.
For more information about how to move data between S3 storage classes automatically, see Managing your storage lifecycle.
For more information about S3 storage classes, see Using Amazon S3 storage classes.
C Store the data in an Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volume. Create snapshots. Store the snapshots in an Amazon S3 bucket.
Incorrect. This solution is not the most cost-effective solution because it requires the use of Amazon EBS in addition to Amazon S3.
For more information about EBS snapshots, see Amazon EBS snapshots.
D Store the data in an Amazon S3 bucket. Use an S3 Lifecycle policy to move the data to S3 Standard-Infrequent Access (S3 Standard-IA).
Incorrect. The storage of the data in an S3 bucket provides a cost-effective initial location for the data. However, S3 Standard-IA is not the most cost-effective storage class to meet the requirements in the scenario. The S3 Glacier storage class is designed for low-cost data archiving.
For more information about S3 storage classes, see Using Amazon S3 storage classes.
Correct
B
B
4.1 Identify cost-effective storage solutions This Question: 00:42 Total: 16:15
18/20 85.0% complete
A media company is designing a new solution for graphic rendering. The application requires up to 400 GB of storage for temporary data that is discarded after the frames are rendered. The application requires approximately 40,000 random IOPS to perform the rendering.
What is the MOST cost-effective storage option for this rendering application?
Report Content Errors
A A storage optimized Amazon EC2 instance with instance store storage
Correct. SSD-Backed Storage Optimized (i2) instances provide more than 365,000 random IOPS. The instance store has no additional cost, compared with the regular hourly cost of the instance.
For more information about pricing for EC2 instances, see Amazon EC2 pricing.
B A storage optimized Amazon EC2 instance with a Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1 or io2) Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volume
Incorrect. Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1 or io2) EBS volumes can deliver more than the 40,000 IOPS that are required in the scenario. However, this solution is not as cost-effective as an instance store because Amazon EBS adds cost to the hourly instance rate. This solution provides persistence of data beyond the lifecycle of the instance, but persistence is not required in this use case.
For more information about Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1 or io2) EBS volumes, see Provisioned IOPS SSD volumes.
For more information about pricing for Amazon EBS, see Amazon EBS pricing.
C A burstable Amazon EC2 instance with a Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volume
Incorrect. Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) EBS volumes are engineered to maximize the throughput of data that can be sent to and from a volume, not the random IOPS. Consequently, this solution does not meet the IOPS requirement. In addition, Amazon EBS adds cost to the hourly instance rate. This solution provides persistence of data beyond the lifecycle of the instance, but persistence is not required in this use case.
For more information about Throughput Optimized HDD (st1) EBS volumes, see Throughput Optimized HDD volumes.
For more information about pricing for Amazon EBS, see Amazon EBS pricing.
D A burstable Amazon EC2 instance with Amazon S3 storage over a VPC endpoint
Incorrect. The rapidly changing data that is required for the scratch volume space makes Amazon S3 (object storage) the wrong storage. Block storage is appropriate for the read/write functionality to work smoothly.
Incorrect
B
A
4.2 Identify cost-effective compute and database services This Question: 01:00 Total: 17:15
19/20 90.0% complete
A company is deploying a new application that will consist of an application layer and an online transaction processing (OLTP) relational database. The application must be available at all times. However, the application will have periods of inactivity. The company wants to pay the minimum for compute costs during these idle periods.
Which solution meets these requirements MOST cost-effectively?
Report Content Errors
A Run the application in containers with Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) on AWS Fargate. Use Amazon Aurora Serverless for the database.
Correct. When Amazon ECS uses Fargate for compute, it incurs no costs when the application is idle. Aurora Serverless also incurs no compute costs when it is idle.
For more information about Fargate, see AWS Fargate Pricing.
For more information about Aurora Serverless, see Amazon Aurora Serverless.
B Run the application on Amazon EC2 instances by using a burstable instance type. Use Amazon Redshift for the database.
Incorrect. EC2 burstable instances offer burstable capability without scaling. However, this solution does not minimize cost during the periods of inactivity and is not the most cost-effective option. In addition, an Amazon Redshift database is not ideal for OLTP. Amazon Redshift is specifically designed for online analytic processing (OLAP).
For more information about Amazon Redshift, see What is Amazon Redshift?
C Deploy the application and a MySQL database to Amazon EC2 instances by using AWS CloudFormation. Delete the stack at the beginning of the idle periods.
Incorrect. Although infrastructure as code (IaC) helps with availability, this solution does not meet the requirement of being always available. In addition, this solution offers no way to keep the database data after the database is recreated.
For more information about CloudFormation, see What is AWS CloudFormation?
D Deploy the application on Amazon EC2 instances in an Auto Scaling group behind an Application Load Balancer. Use Amazon RDS for MySQL for the database.
Incorrect. With this solution, at least one instance and a database will run during the periods of inactivity. This solution does not minimize cost during the periods of inactivity. This solution is not the most cost-effective option.
For more information about Auto Scaling groups, see What is Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling?
4.3 Design cost-optimized network architectures
Question 20
A company that processes satellite images has an application that runs on AWS. The company stores the images in an Amazon S3 bucket. For compliance reasons, the company must replicate all data once a month to an on-premises location. The average amount of data that the company needs to transfer is 60 TB.
What is the MOST cost-effective way to transfer this data?
Report Content Errors
A Export the data monthly from the existing S3 bucket to an AWS Snowball Edge Storage Optimized device. Ship the device to the on-premises location. Transfer the data. Return the device a week later.
Correct. The base price covers the device and 10 days of usage at the on-premises location. If the company returns the device within a week, the company pays the base price and the price for data transfer out of AWS.
For more information about Snowball pricing, see AWS Snowball Pricing.
B - Use S3 bucket replication to copy all objects to a new S3 bucket that uses S3 Standard-Infrequent Access (S3 Standard-IA) storage. Use an AWS Storage Gateway File Gateway to transfer the data from the new S3 bucket to the on-premises location. Delete the images from the new S3 bucket after the transfer of the data.
Incorrect. There is no cost advantage if the company copies all the data to another S3 bucket that uses S3 Standard-IA storage. The company could transfer the data directly from the original S3 bucket. This solution is not the most cost-effective option because the additional replication increases the cost.
For more information about data transfer pricing for Storage Gateway, see AWS Storage Gateway pricing.
C - Use S3 bucket replication to copy all objects to a new S3 bucket that uses S3 Standard-Infrequent Access (S3 Standard-IA) storage. Use Amazon S3 to transfer the data from the new S3 bucket to the on-premises location. Delete the images from the new S3 bucket after the transfer of the data.
Incorrect. There is no cost advantage if the company copies all the data to another S3 bucket that uses S3 Standard-IA storage. The company could transfer the data directly from the original S3 bucket. This solution is not the most cost-effective option because the additional replication increases the cost.
For more information about S3 data transfer pricing, see Amazon S3 pricing.
D - Create an Amazon CloudFront distribution for the objects in the existing S3 bucket. Download the objects from CloudFront to the on-premises location every month.
Incorrect. Data transfer to CloudFront is free of cost, but data transfer of 60 TB from CloudFront to an on-premises location incurs a cost. This option would cost approximately twice as much as the option to use the AWS Snowball Edge Storage Optimized device.
For more information about CloudFront data pricing, see Amazon CloudFront Pricing.